Storage#
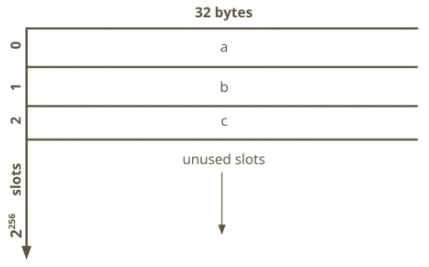
The storage is a mapping from a key to a value. The number of keys is for all practical purposes infinite. The value can be up to 32 bytes. Every value is initialized with a 0.
This is like the SSD in your computer. Storage is non-volatile.
source: https://docs.alchemy.com/docs/smart-contract-storage-layout
We will represent the storage as a dictionary.
class KeyValue:
def __init__(self): self.storage = {}
def load (self, key) : return self.storage[key]
def store(self, key, value): self.storage[key] = value
Warm/Cold#
It costs different amount of gas whether we access a warm or cold storage slot.
A slot is said to be warm if it was access before. Otherwise it is cold.
Accessing a slot that is cold costs more gas than accessing a warm slot.
We implement that logic by keeping track of a cache. When we load a storage slot we save its key in that cache. If a key is in that cache it is said to be warm.
class Storage(KeyValue):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.cache = []
def load(self, key):
warm = True if key in self.cache else False
if not warm: self.cache.append(key)
if key not in self.storage: return 0x00
return warm, super().load(key)
storage = Storage()
We store 420 in storage slot 1
storage.store(1, 420)
Notice how the first time retrieving something from storage slot 1 its cold
storage.load(1)
(False, 420)
Now storage slot 1 is warm
storage.load(1)
(True, 420)
Reading a random storage that was not set to any value will return 0 and not throw an exception.
storage.load(42069)
0